The present invention relates to enhanced methods and systems for the safe storage, handling, and application of caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) in liquid form. Sodium hydroxide is a widely used industrial chemical, typically supplied in aqueous solutions of varying concentrations.
Caustic Soda Liquids
Abstract
However, its high corrosivity, reactivity with carbon dioxide, and tendency to crystallize under specific conditions present operational challenges. The invention introduces improved formulations and containment strategies to mitigate these issues, ensuring safer transport, prolonged stability, and more efficient dosing. This solution is applicable across numerous sectors including chemical manufacturing, water treatment, food processing, and oil refining.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Caustic soda (NaOH), also known as sodium hydroxide, is a highly caustic and reactive alkaline substance used extensively in industrial processes. It is most commonly distributed as a liquid solution, typically in concentrations of 25%, 32%, or 50%. Its strong alkalinity and effectiveness in neutralizing acids make it indispensable in a broad range of chemical and manufacturing applications.
Despite its widespread use, the storage and handling of caustic soda liquids present several difficulties. NaOH is highly corrosive to skin and most metals, and it readily absorbs moisture and carbon dioxide from the air, leading to the formation of solid sodium carbonate, which can cause blockages in pipes and dosing systems. Furthermore, under colder temperatures, sodium hydroxide tends to crystallize, which poses additional problems in transport and storage infrastructure.
Caustic Soda
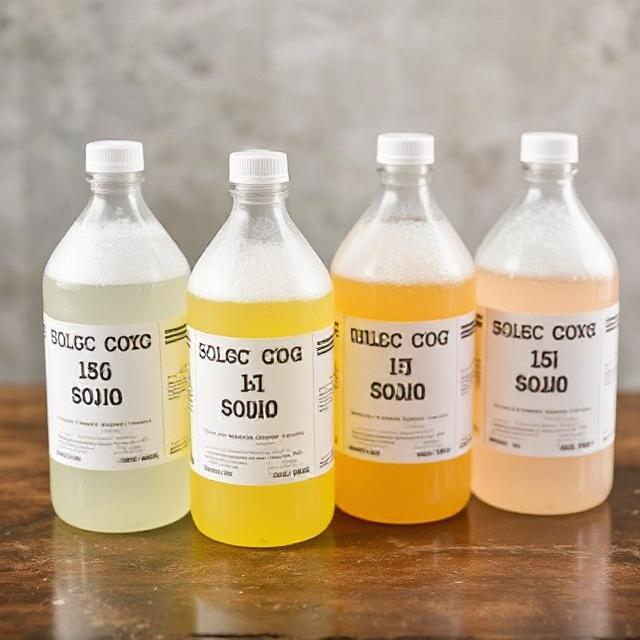

-
Caustic soda is one of the most important and widely used industrial chemicals in the world. Key uses include:
-
Water and Wastewater Treatment
-
Chemical Manufacturing
-
Pulp and Paper Industry
-
Petroleum Industry
-
Food and Beverage Industry
-
Textile Industry
-
Soap and Detergent Manufacturing
-
Aluminum Production
Due to its versatility, caustic soda is a key component in both basic industrial processes and high-precision chemical applications. The invention seeks to ensure its safer, more stable, and more efficient use across all these domains.
-